Functional overview¶
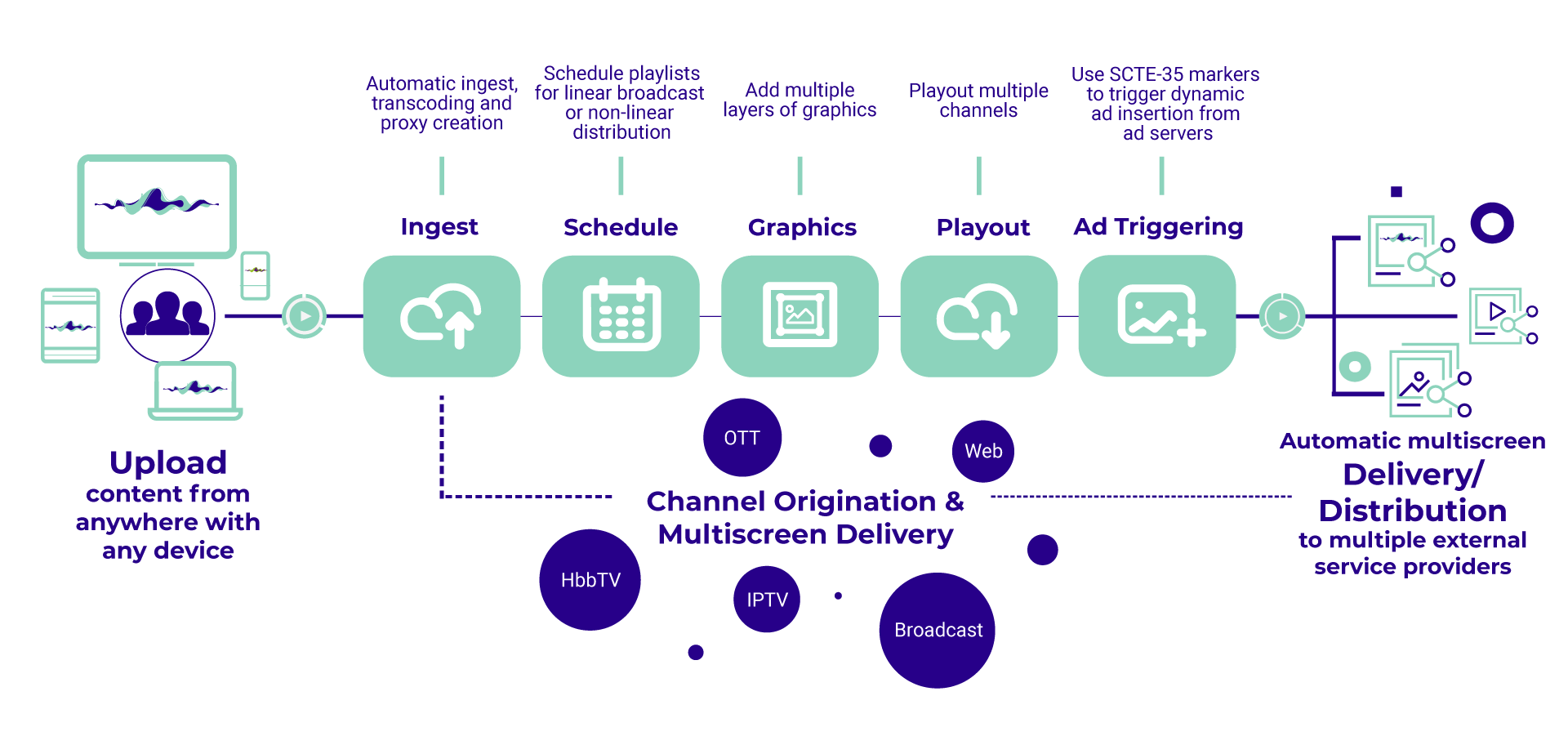
The following graphic shows the basic workflow when using Makalu:
From a high-level perspective, Makalu consists of the following functional areas:
- Ingest
- Schedule (Traffic/Planning)
- Graphics
- Playout (Automation)
- Ad triggering (optional)
Ingest¶
The ingest functionality provided by Makalu is focused on the file-based upload of video content. To upload files, the included Asset Uploader application can be used. Uploaded video files are automatically processed, which includes, for example, the creation of a thumbnail image, a low-res (proxy) video file, and media information (technical metadata). As a result, the processed files can be used properly by Makalu. In addition to file-based content, Makalu also supports live sources. For more information, see the section Ingest.
Schedule¶
Makalu includes a traffic component for both strategic and operational planning, as well as for rough and detailed daily planning. It enables the use of uploaded files as primary events to create shows, adding shows to playlists, as well as adding graphics and other secondary events. A playlist can be added to the rundown in the Makalu Automation to define the content the playout should actually play. For more information, see the section Schedule.
Graphics¶
Makalu uses the Singular.Live graphics platform for overlay graphics, which provides tools for composing, controlling, and output of professional graphics. Each output generated by Singular.Live can be received by Makalu Automation and used as an additional layer on top of the main video output. For more information, see the section Graphics.
Playout¶
The Makalu Automation component is used to control one or more players running on playout nodes, which seamlessly play video files or live sources from a playlist. The automation can be controlled either manually by the operator or scheduled/time-triggered via the planning component. The player output can be distributed to web, OTT, and IPTV targets. For more information, see the section Automation.